Cat of the Month ~ September 2009
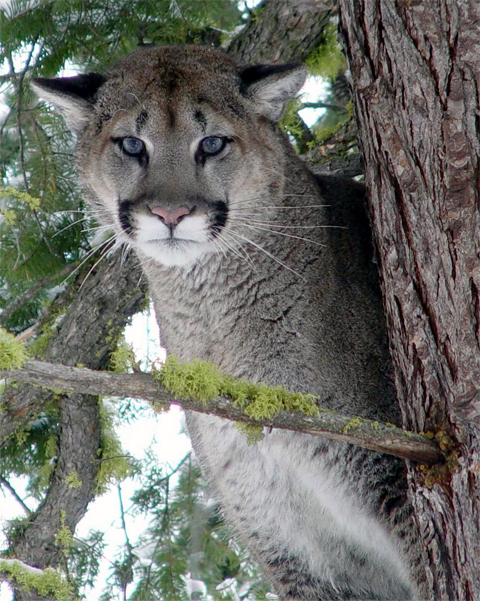

The Cougar is also known as puma, mountain lion, Catamount, or panther, depending on the region in which it is identified, is a mammal of the Felidae family (in other words it’s a Cat :yes: ahem..), native to the Americas.
This large, solitary creature has the greatest range of any large wild terrestrial mammal in the Western Hemisphere, extending from Yukon in Canada to the southern Andes of South America. An adaptable, generalist species, the cougar is found in every major American habitat type. It is the second heaviest cat in the American continents after the jaguar, and the fourth heaviest in the world, along with the leopard, after the tiger, lion, and jaguar, although it is most closely related to smaller felines.
The genus and species name is said to mean ‘a cat of one color’, describing the almost single colored coat. Coat colors range from tan to dark brown, depending on the region. Coat thickness also varies. Kittens are born with spotted coats as are lion cubs. They also have the distinguishing black face marks and tail tip. As the young cougar matures, it will lose it’s spots for an adult coat. Cougars range in size from five to eight feet long, and from about 60 to 225 lbs. Males are almost twice as large as females.
A capable stalk-and-ambush predator, the cougar pursues a wide variety of prey. Primary food sources include deer, elk, and bighorn sheep, as well as domestic cattle, horses, and sheep, but it also surprisingly hunts species as small as insects and rodents. Moreover, it prefers habitats with dense underbrush and rocky areas for stalking, but it can live in open areas.
The cougar is territorial and persists at low population densities. Individual territory sizes depend on terrain, vegetation, and abundance of prey. While it is a large predator, it is not always the dominant species in its range, as when it competes for prey with other predators such as the jaguar, gray wolf, American Black Bear, and the grizzly bear. It is a reclusive cat and usually avoids people. Attacks on humans remain rare, despite a recent increase in frequency.
Due to excessive hunting following the European colonization of the Americas, and continuing human development of cougar habitat, populations have dropped in most parts of its historical range. In particular, the cougar was eradicated in eastern North America, except an isolated sub-population in Florida; the animal may be recolonizing parts of its former eastern territory. With its vast range, the cougar has dozens of names and various references in the mythology of the indigenous Americans and in contemporary culture.
The Cougar has recently made a comeback in the state of Wyoming, where it presently has the largest population in North America.