Cat of the Month ~ March 2018
Cat Soohorang of PyeongChang
Cat of the Month ~ February 2018
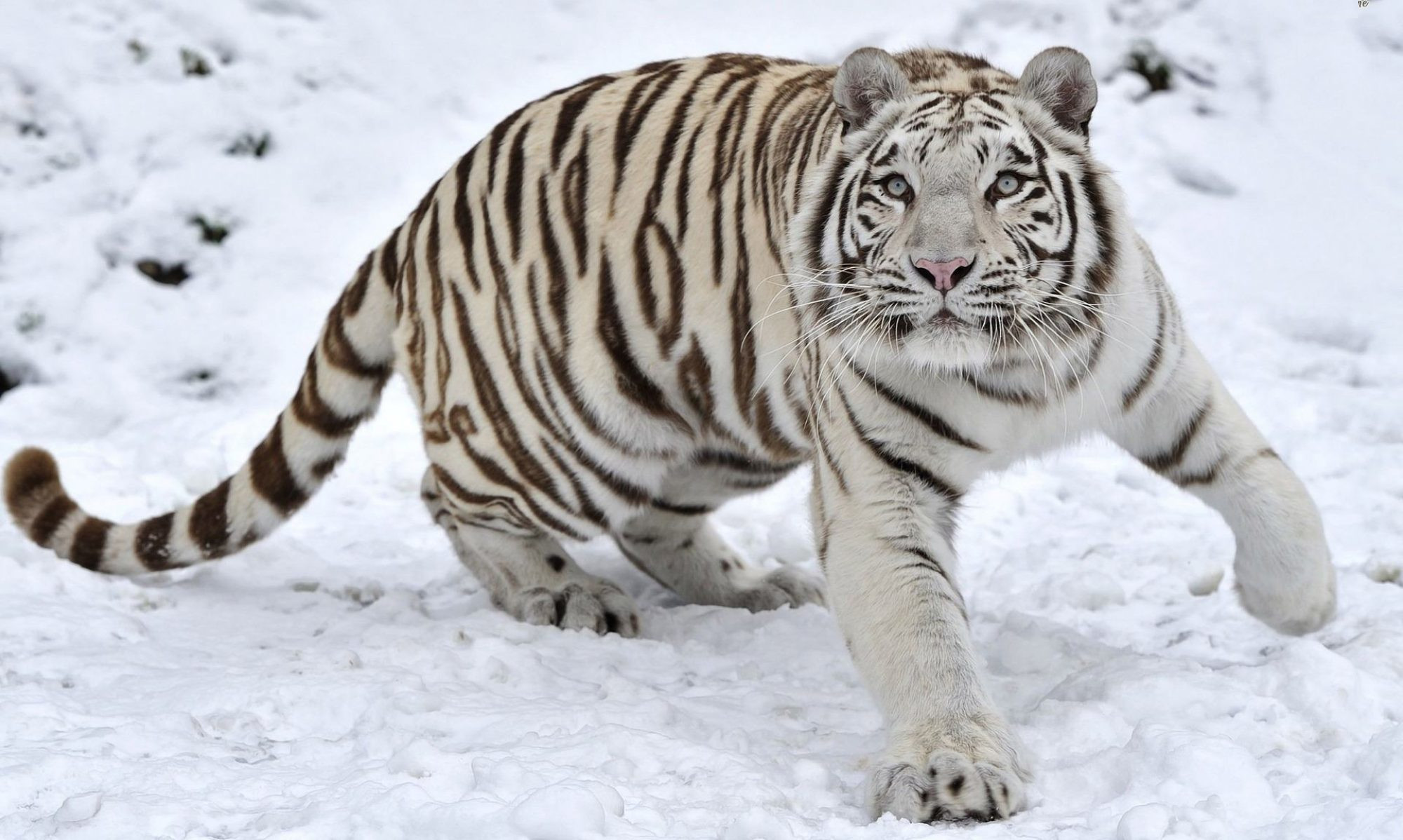
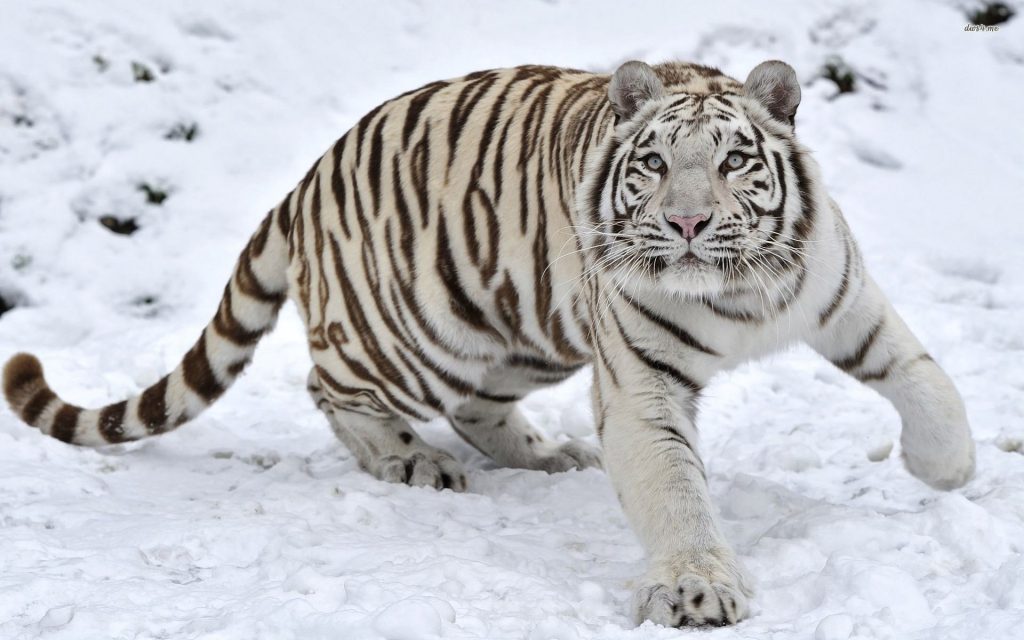
Soohorang the cat is the Olympic Winter Games mascot. He is the Official mascot of the 2018 Winter Olympics (9-25 Feb) and of the Paralympics (9-18 Mar) in PyeongChang, South Korea.

Soohorang, the Olympic mascot, made his debut in July 2017, during Olympic events in both Seoul and PyeongChang. Gunilla Lindberg, Chair of the IOC Coordination Commission for the Olympic Winter Games PyeongChang 2018, said of choosing a white tiger to be the 2018 Olympic mascot,
It’s a beautiful animal, strongly associated with Korean culture. It also symbolises the close link between the Olympic Winter Games and the natural environment. I’m sure the new mascot will be very popular with Koreans and people around the world.
Athletes who win medals at the Pyeongchang Winter Olympics are honored in two separate ceremonies, according to the International Olympic Committee (IOC). The first one happens directly after the event, and is when the athletes get their stuffed tiger….”instead of flowers, medalists are being given a doll of the Games’ mascot Soohorang.” The origin of the motif is the famous (and endangered) South Korean white tiger. The white tiger has been long considered Korea’s guardian animal.
“Sooho”, meaning protection in Korean, symbolises the protection offered to the athletes, spectators and other participants of the 2018 Games.
“Rang” comes from the middle letter of “Ho-rang-i”, the Korean word for “tiger,” and is also the last letter of “Jeong-seon A-ri-rang”,
a cherished traditional folk song of Gangwon Province, where the Games will be held.
Soohorang not only has a challenging spirit and passion, but is also a trustworthy friend who protects the athletes, spectators and all the participants of the Olympic Games.
Well worth being cat of the month then Eh Osc?
And just to round this all off nicely (we hope) here are a few more images relating to our friendly cat Soohorang.




The Kodkod cat
Cat of the Month ~ January 2018
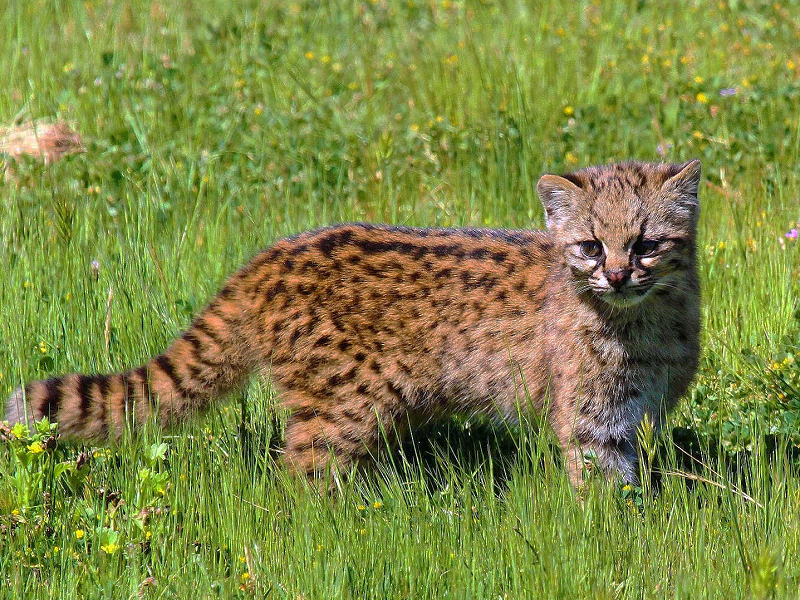
The tiny Kodkod Cat or Guigna (Oncifelis guigna) is one of the worlds smallest and least known cats, and is in fact the smallest cat in the entire land mass of North and South America combined.
These felines are found in central and southern Chile, from Santiago to Parque Nacional Laguna San Rafael (a distance of well over 2000 kilometers), and also in western Argentina (generally on the west coast of South America). Information about the ecology of Kodkod is largely anecdotal. Guignas have one of the smallest geographical distributions known for any felid, and therefore any information gathered by scientists or local people can improve our knowledge and assist in further steps in conservation.
The kodkod has a small head, large feet, and a thick tail. The length of a typical adult is around 45 centimetres, with a short 20 to 25 centimetres tail and a shoulder height of about 25 centimetres. The weight of a fully grown animal is between 2 to 2.5 kilograms (5 pounds).
The coat has a base color ranging from brownish-yellow to grey-brown. Guignas have black spotted gray fur, black dorsal stripes on their necks, and bushy, banded tails. The body is decorated with dark spots, with a pale underside and a ringed tail. The ears are black with a white spot, while the dark spots on the shoulders and neck almost merge to form a series of dotted streaks. Melanistic Kodkods with spotted black coats are quite common.
Kodkods are strongly associated with mixed temperate rainforests of the southern Andean and coastal ranges, particularly the Valdivian and Araucaria forests of Chile. These forests are noted as having bamboo spread under the tree canopy. These evergreen temperate rainforest habitats are the preferred areas for the Kodkod as they are less damp than deciduous temperate moist forests and coniferous forests. They are versatile and tolerant of altered habitats, being found in secondary forest and shrub as well as in primary forest. They will even be found on the fringes of settled and cultivated areas. In Argentina, for example, they have been recorded hunting in moist montane or mountainous forest, not thier preferred region, ranging up to the treeline at approximately 1,900 m (6,200 ft) in this and other areas.
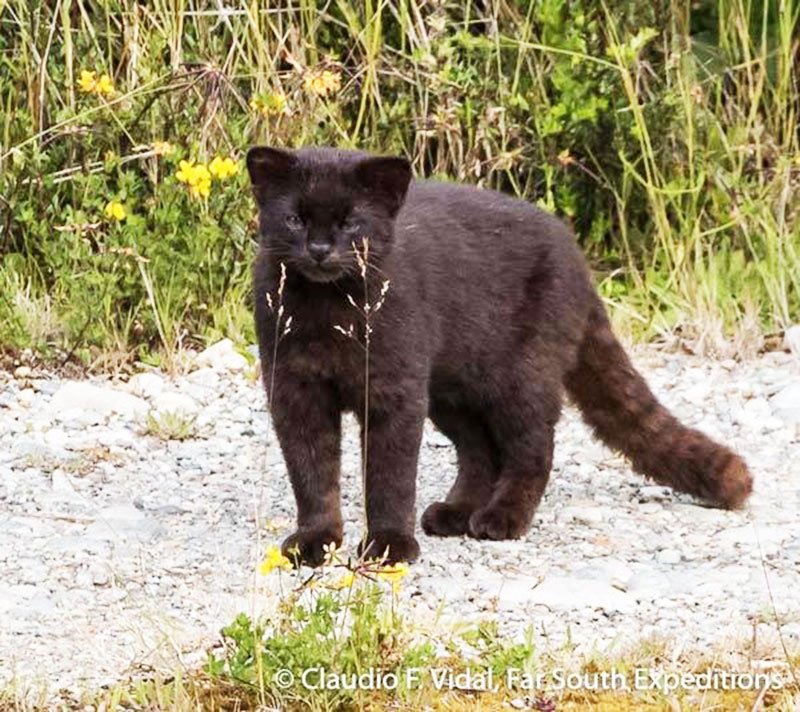

Kodkods are equally active during the day as during the night, although they only venture into open terrain under the cover of darkness. During the day, they rest in dense vegetation in ravines, along streams with heavy cover, and in piles of dead gorse. They are excellent climbers, and easily able to climb trees more than a meter in diameter. On the ground they stalk abd hunt birds, lizards and rodents in the ravines and forested areas, feeding on southern lapwing, austral thrush, chucao tapaculo, huet-huet, domestic geese and chicken.
In studies carried out it has been reported that male Kodkods maintain exclusive territories 1.1 to 2.5 square kilometres in size, while females occupy smaller ranges of just 0.5 to 0.7 square kilometres.
Whilst breeding, the gestation period lasts for around 75 days and the average litter size is one to three kittens. Also, they are known to live until they are around 11 years old.
The major threat to the Kodkod is logging of its temperate moist forest habitat, and the spread of pine forest plantations and agriculture, particularly in central Chile. In 1997 to 1998, two out of five radio-collared Kodkods were killed on Chilo Island whilst attempting to gain food from chicken coops.
There are two known subspecies of this cat:
- Leopardus guigna guigna – found in Southern Chile and Argentina
- Leopardus guigna tigrillo – found in Central Chile
The kodkod was formerly considered a member of the genus Oncifelis, which consisted of three small feline species native to South America. All of these species have now been moved into the genus Leopardus. Along with the Kodkod, the former members of Oncifelis were the Colocolo and Geoffroy’s cat.
Another Vulnerable Animal:
Like the Iriomote Cat featured in our blog of July last year, the Kodkod cat is an endangered feline. Since 2002, it has been listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List as the total effective population may comprise less than 10,000 mature individuals, and is threatened due to persecution, loss of habitat and its prey base.
Source: From Wikipedia & others
References:
1. BBC Television. Big Cats – Episode Listing (2018)
2. Small Wildcats. http://smallwildcats.com/ Please donate on this site ~ if you can afford it!
3. Book. Natural history and landscape-use of Guignas on isla Grande De chiloé, Chile
Author(s): Jim Sanderson, Mel E. Sunquist, and Agustin W. Iriarte, Source: Journal of Mammalogy
Under the Christmas Tree
Foldex
The Foldex cat breed was established by cross breeding both Exotic Shorthair and Exotic Longhair breeds with the Scottish Fold breed – it’s distinguishing feature (which characterises the Foldex breed) is a highly rounded, gathered and folded pair of ears.
Cat of the Month ~ December 2017
The Foldex breed first appeared around 1992 in Quebec, Canada as an experimental breed. This cross breeding resulted is a new Persian type breed with folded ears. This animal made its first appearance in a show hall in 1993, being presented by Betty Ann Yaxley. On viewing and admiring this new feline Jeanne Barrette dedicated herself to work with this animal well into the future. Consequently the Foldex breed was accepted as an ‘Experimental Breed’ in November of 1998 and in August of 2006 it was accepted as a New Breed for championship (cat show) status. However it is only recognised by the Canadian Cat Association (CCA).
The Foldex breed has a shorter nose than the Scottish Fold breed. Their body type is sturdy and muscular with good bone structure, a stubby neck, round eyes and a round head that give the breed a very owl like appearance. The folded ears further make the cat a little like a small ‘teddy bear’. Fully grown the weight of this cat is around five to eight pounds. Coats are dense and soft to the touch and can be long or short. The Foldex breed comes in a large variety of colours and patterns.
If allowed to breed these folded ear cats must be crossed with a straight ear cat. This must be done to avoid the potential skeletal defects associated with the breed.
Suprisingly, all Foldex breed kittens are born with straight ears. At three to four weeks the ears begin to start to bend and then fold on many of these kittens.
Many vets recommend that ears will require special cleaning care to prevent infections such as might living in the ear canal.
These felines are highly intelligent, inquisitive (of course), loving and noble cats. The make good house cats as they have a calm and docile temperament (close to that of the Exotic). While they are mostly quiet they often do like to get envolved with what’s going on in the house. The also like to play and interact with us humans when thye are in the mood.
The King O’ The Cats
The King o’ the Cats is a folk tale from the British Isles. The earliest known example is found in Beware the Cat, written by William Baldwin in 1553, though this story itself is
related to the first century story of “The Death of Pan”.
Other notable versions of this cat tale include one in a letter written by Thomas Lyttelton first published in 1782.
M. G. (Monk) Lewis the English novelist and dramatist, told the story to Percy Bysshe Shelley in 1816, and a further version was adapted by Joseph Jacobs, the Australian folklorist and writer, from several sources, including one collected by Charlotte S. Burne (the first woman president of the Folklore Society).
Walter Scott reported that ‘the King O’ The Cats’ was a well known nursery tale in the Scottish Highlands in the eighteenth century. It can be categorised as a “death of an elf (or cat)”. It is a common type of tale you can look up on the webpage Aarne-Thompson-Uther Classification of Folk Tales
“Well Osc I never knew that an “elf” was a cat! …. mind you you’re a bit of an impish elf yourself on occasion”
On to the story…I suggest you turn down the lights…and turn off all distractions … :- )
The King O’ The Cats
One winter’s evening the sexton’s wife was sitting by the fireside with her big black cat, Old Tom, on the other side, both half asleep and waiting for the master to come home.
They waited and they waited, but still he didn’t come, till at last he came rushing in, calling out, ‘Who’s Tommy Tildrum?’ in such a wild way that both his wife and his cat stared at him to know what was the matter.
‘Why, what’s the matter?’ said his wife, ‘and why do you want to know who Tommy Tildrum is?’
‘Oh, I’ve had such an adventure. I was digging away at old Mr Fordyce’s grave when I suppose I must have dropped asleep, and only woke up by hearing a cat’s Miaou.’
‘Miaou!’ said Old Tom in answer.
‘Yes, just like that! So I looked over the edge of the grave, and what do you think I saw?’
‘Now, how can I tell?’ said the sexton’s wife.
‘Why, nine black cats all like our friend Tom here, all with a white spot on their chestesses. And what do you think they were carrying? Why, a small coffin covered with a black velvet pall, and on the pall was a small coronet all of gold, and at every third step they took they cried all together, Miaou — ‘
‘Miaou!’ said Old Tom again.
‘Yes, just like that!’ said the sexton; ‘and as they came nearer and nearer to me I could see them more distinctly; because their eyes shone out with a sort of green light. Well, they all came towards me, eight of them carrying the coffin, and the biggest cat of all walking in front for all the world like — but look at our Tom, how he’s looking at me. You’d think he knew all I was saying.’
‘Go on, go on,’ said his wife; ‘never mind Old Tom.’
‘Well, as I was a-saying, they came towards me slowly and solemnly, and at every third step crying all together, Miaou –‘
‘Miaou!’ said Old Tom again.
‘Yes, just like that, till they came and stood right opposite Mr Fordyce’s grave, where I was, when they all stood still and looked straight at me. I did feel queer, that I did! But look at Old Tom; he’s looking at me just like they did.’
‘Go on, go on,’ said his wife; ‘never mind Old Tom.’
‘Where was I? Oh, they stood still looking at me, when the one that wasn’t carrying the coffin came forward and, staring straight at me, said to me — yes, I tell ‘ee, said to me, with a squeaky voice, “Tell Tom Tildrum that Tim Toidrum’s dead,” and that’s why I asked you if you knew who Tom Tildrum was, for how can I tell Tom Tildrum Tim Toldrum’s dead if I don’t know who Tom Tildrum is?’
‘Look at Old Tom, look at Old Tom!’ screamed his wife.
And well he might look, for Tom was swelling and Tom was staring, and at last Tom shrieked out, ‘What — old Tom dead! then I’m the King o’ the Cats!’ and rushed up the chimney and was nevermore seen.
trad.
Blackie
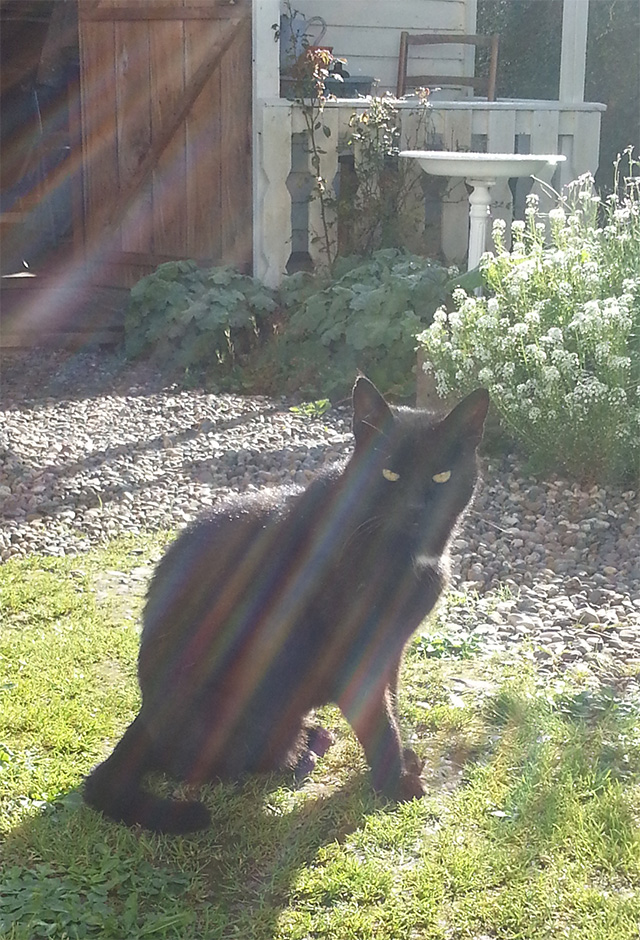
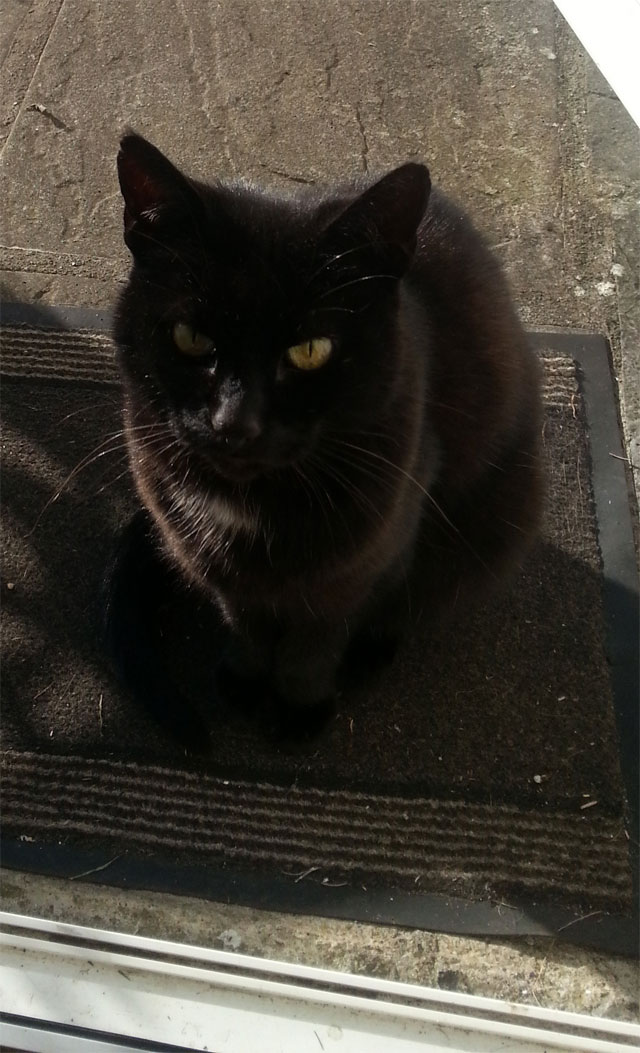
Cat of the Month ~ September 2017
Blackie is a faithful 3 year old domestic cat with great hunting ability. She lives in County Roscommon in the republic of Ireland where life is peaceful and slow for most. But if you are a bird or a mouse you’d better have your wits about you when Blackie is about!
She is often seen depositing little presents on her cottage doorstep, accompanied by great howls of “look at me” and “a’rnt I a clever puss”.
Hey Osc, you could learn a thing or two from this here puss