Northern Tiger cats (Leopardus tigrinus) were previously referred to as Oncillas, Tigrinas, Small-spotted cats or Tiger cats. In 2013 after genetic testing, the Oncilla was split into two species and they are now referred to as either Northern Tiger Cats or Southern Tiger Cats Leopardus guttulus.
Tiger cats are one of the smallest cat species in the Americas, averaging just 2.5 kg but in some cases reaching a maximum weight of 3.5 kg. These larger cats are usually males.
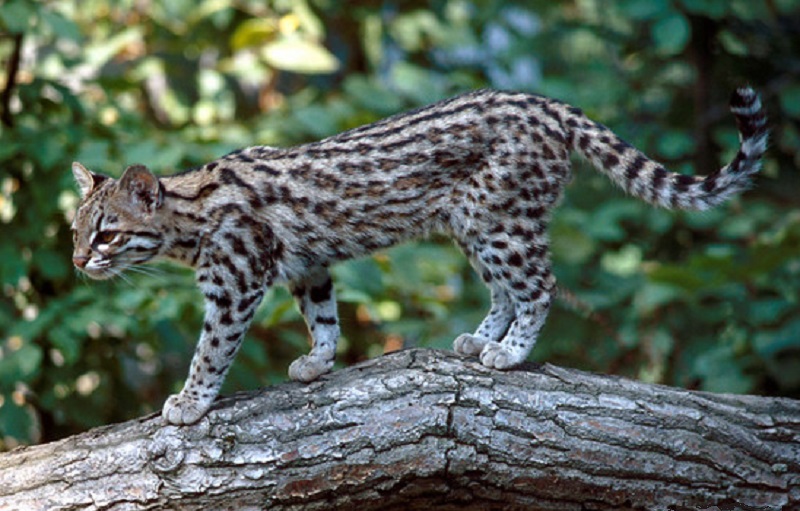

They are delicatly built, with a narrow head and large ears. They have a black rear end with a central white spot. Their eyes have a white line above an eye colour of golden or light brown. The large ears have are black ‘outside’ with a central white spot.
Northern Tiger cats are pale yellow to ochre or grey, marked by small dots that tend to form an open rosette. Melanism is common. The paler belly fur is covered with dark spots. The fur is firm, lies close to the skin and does not turn forward in the nape region as it does on the Ocelot and Margay. Limbs are spotted on the outside and the long tail has spots at the root, developing into a thinly ringed tail with a black tip.
They are found in a range from Costa Rica and Panama in Central America into South America up to Central Brazil. Its southern limits are not yet well known, as well as the extent of a possible overlap with the populations of the Southern Tiger cat. Its distribution in the Amazon basin is possibly patchy and not continuous. The Northern Tiger cat is absent from Colombia, Venezuela, and Paraguay. From Ecuador and Peru, only few museum specimens exist and only in 2000 the species was formally confirmed in Bolivia through live-trapping.
Northern Tiger cat population densities are very low throughout most of its range. For example in the Amazon, usually the safeguard region for the tropical American felids, the Northern Tiger cat occurs at exceedingly low densities of perhaps only 0.01 individuals per 100 km². There is evidence that it is also naturally rare and elusive in Central America and some areas of Brazil.
The Northern Tiger cat lives in a wide range of forest habitats, semi-arid thorny scrub, savannah and wet/swampy savannah. In Central and northwestern South America, it is mainly associated with montane cloud forests, where it is usually found at higher elevations than the Ocelot and Margay. Even though it is found in Amazonian rainforests it is not clear to what degree they use this habitat. It can be found in disturbed habitats, even close to human settlements, as long as there is natural cover and a source of food.
As a generalist carnivore and the largest and most adaptable of the small cat species in tropical America, the Ocelot dominates the other small cat species. In areas where the Ocelot occurs, species like the Northern Tiger cat avoid those areas because of the threat of predation. This negative effect on other small cat species is called the “ocelot effect”.

The Northern Tiger cat is a solitary felid. It is active predominantly at night, but can also show varying degrees of diurnal activity. This activity during any time of the day is suggested to be a strategy to avoid the Ocelot. On the other hand, Tiger cat numbers are not affected by the presence of the Margay and Jaguarundi, which are more likely potential competitors for similar sized prey.
Tiger cats are excellent climbers, but spend most of their time on the ground as most of their prey is terrestrial. When threatened, they show an aggressive behavior with arched back and raised hair, besides showing the teeth and producing a “whistling-spiting” vocalization.
The Northern Tiger cat’s diet is still very poorly studied, but is known to be based on small mammals such as rodents, birds and reptiles.
As is common with many animals, the threats to life are many:
- habitat loss and fragmentation
- persecution by humans
- killing due to poultry depredation
- vehicle collisions on roads
- exposure to domestic carnivore diseases
Conservation
The Northern Tiger cat is classified as Endangered in Brazil and Vulnerable in Colombia. Brazil is the main range country for both the Northern and Southern Tiger cat species.
These cats are protected over part of their range. Hunting is prohibited in Brazil, Colombia, Costa Rica, French Guiana, Suriname and Venezuela, but they are not legally protected in Ecuador, Guyana, Nicaragua, Panama and Peru.
Although the international trade in furs has been heavily reduced, illegal hunting and capturing still takes place, mostly for the local market. Historical trade on tiger cats (which would include both species) from 1976 to 1985 consisted of astonishing 352,508 skins.
See also Southern Tiger Cat
Source: Original Article International Society for Endangered Cats (ISEC) https://wildcatconservation.org/