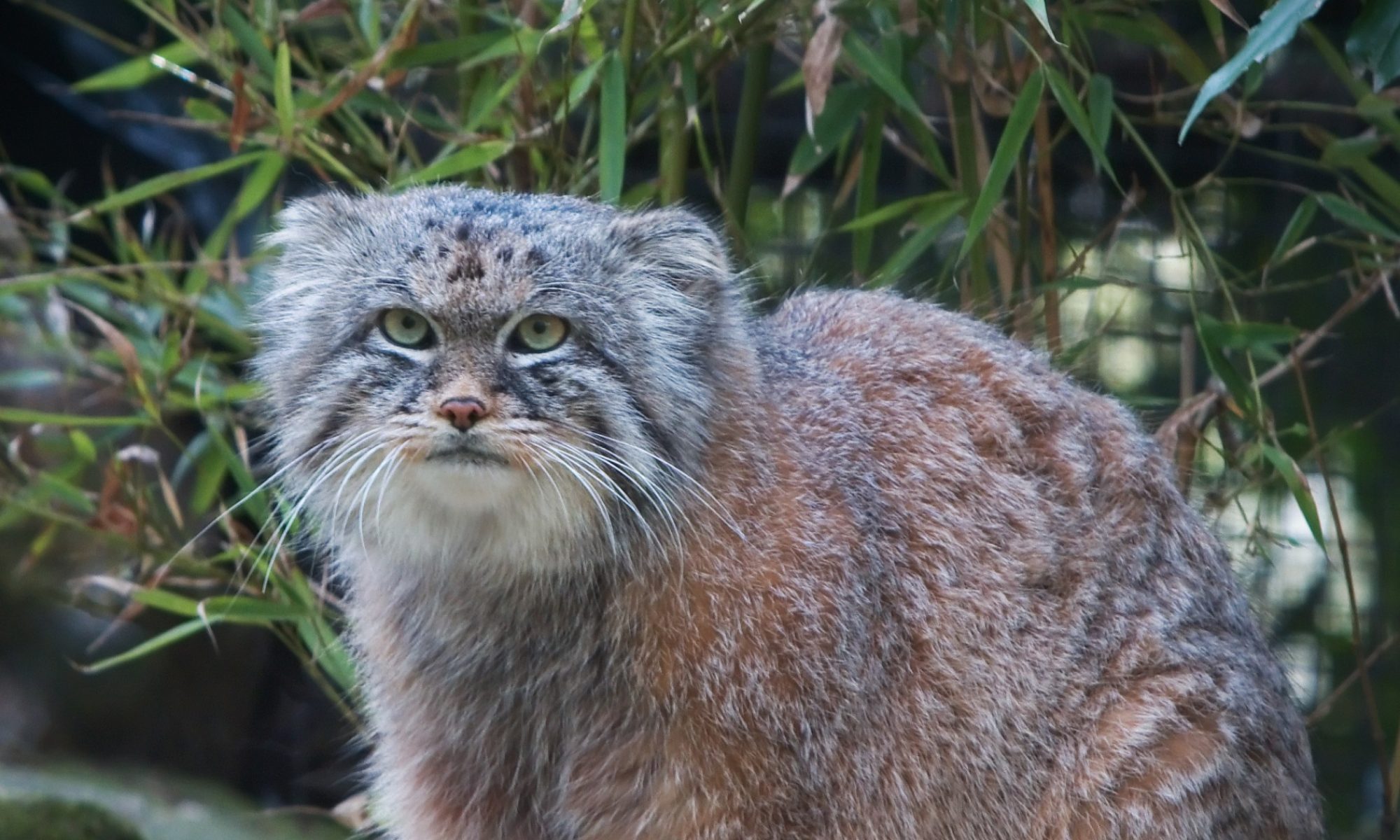
Egyptian Maus are a medium-sized short-haired cat breed. They are the only naturally spotted breed of domesticated cat. The spots on an Egyptian Mau are not just on the coat; a shaved Mau has spots on its skin. The Ocicat is very similar in appearance to the Egyptian Mau, but was the product of selective breeding which led to its spots. Another similar looking breed is the Bengal cat, but this breed tends to be considerably larger.
The breed conformation is described by The Cornell Book of Cats
as a balance between the compactness of a Burmese and the slim elegance of a Siamese. Its medium-length body is muscular, with the hind legs longer than the front, giving the Mau the appearance of standing on tiptoes when upright.
The longer hind legs are another reason for the breed’s startling speed. The Mau also has a loose flap of skin on the lower abdomen, similar to the Cheetah, which allows a longer stride while running, again contributing to its great speed. A Mau running at full speed is impressive, with incredible acceleration.
Maus often possess very musical voices. They are known to chirp, chortle and emit other distinctly unusual vocalizations when stimulated. Another behavior, quite common in happy Maus, has been described as “wiggle-tail.” The cat, male or female, moves its back legs up and down, and appears to be marking territory, also known as spraying, but it is not actually releasing urine. Even veteran Mau owners are known to check after a joyous Mau does this little dance.

Egyptian Mau, likely descendant of African wild cats!
Origins
The Egyptian Mau is often said to be descended from African wild cats, and a descendant of the cats seen in wall paintings of Ancient Egypt. This, while perhaps being partly true, does not reveal the careful breeding that has taken place to create the ‘purebred’ Egyptian Mau, which was only given championship status in some organisations in 1968.
The modern Mau is said to have originated in 1953, Italy, when exiled Russian Princess Natalie Troubetskoy met the cat of the Egyptian Ambassador to Italy. She convinced him to obtain several cats from Egypt for her, and she began to breed them. Maus were attempted to be created in Britain by cross-breeds of Abyssinians, Siamese and tabbies, however these did not resemble the true Maus.
Egyptian Maus will either have a ‘scarab beetle’ or ‘M’ marking on their foreheads – those with the latter tend to be from the United States.
Physical attributes
Egyptian Maus are thought by many to be one of the progenitor breeds of the modern domestic cat. They have anatomical, metabolic and behavioral differences from other cat breeds which could be considered as evidence of antiquity or at least uniqueness from other cat breeds. Besides those already mentioned, Maus are more temperature sensitive than most breeds – they are fond of very warm temperatures. They are more sensitive to medicines and anesthesia. Maus allegedly have an unusually long gestational period. The maximum normal period for cats is 69 days, although Siamese may take a day or two longer. For a Mau, it is said that 73 days is still considered normal. This, however, is not a generally accepted fact, and it is advised for one to assume a 63-67 days gestational period. One should track the cat’s temperature and if it drops by a few degrees without birthing, consult your veterinarian.
Egyptian Maus are the fastest breed of domestic cat, capable of running at 36 mph. The next fastest breed is the American Shorthair which has a top speed of 31 mph. For comparison, giraffes also run at 36 mph. Maus are powerful cats for their size, alert and active. Males are usually somewhat larger than females.
Purebred Egyptian Maus are a relatively rare breed. As of 2007, fewer than 200 kittens are registered with the GCCF each year.[2] As of 2006, a total of 6741 Maus are registered with the CFA. Maus come in five colors. From most to least common these colors are: silver, bronze, smoke, black and blue/pewter.
Black and pewter Maus cannot be shown, but may be used in breeding. All Maus must have green eyes, but an amber cast is acceptable in kittens and young adults up to eighteen months old.
Popular culture
In the 2004 movie Catwoman, the cat ‘Midnight’ who brought Patience Phillips back to life as Catwoman was played by three Egyptian Maus, as well as a computer-generated Mau. The movie reveals that the ancient Egyptian Mau breed has the (fictional) ability to restore life through its connection with the Egyptian goddess Bastet.