Cat of the Month ~ May 2015
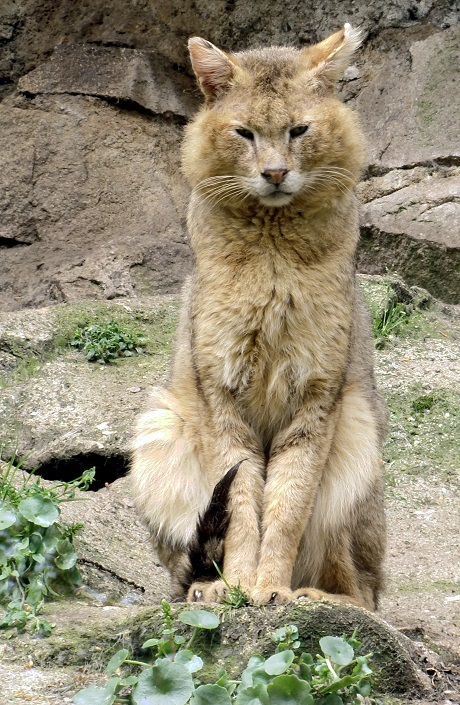

at Pont-Scorff Zoo (Nr Lorient, France)
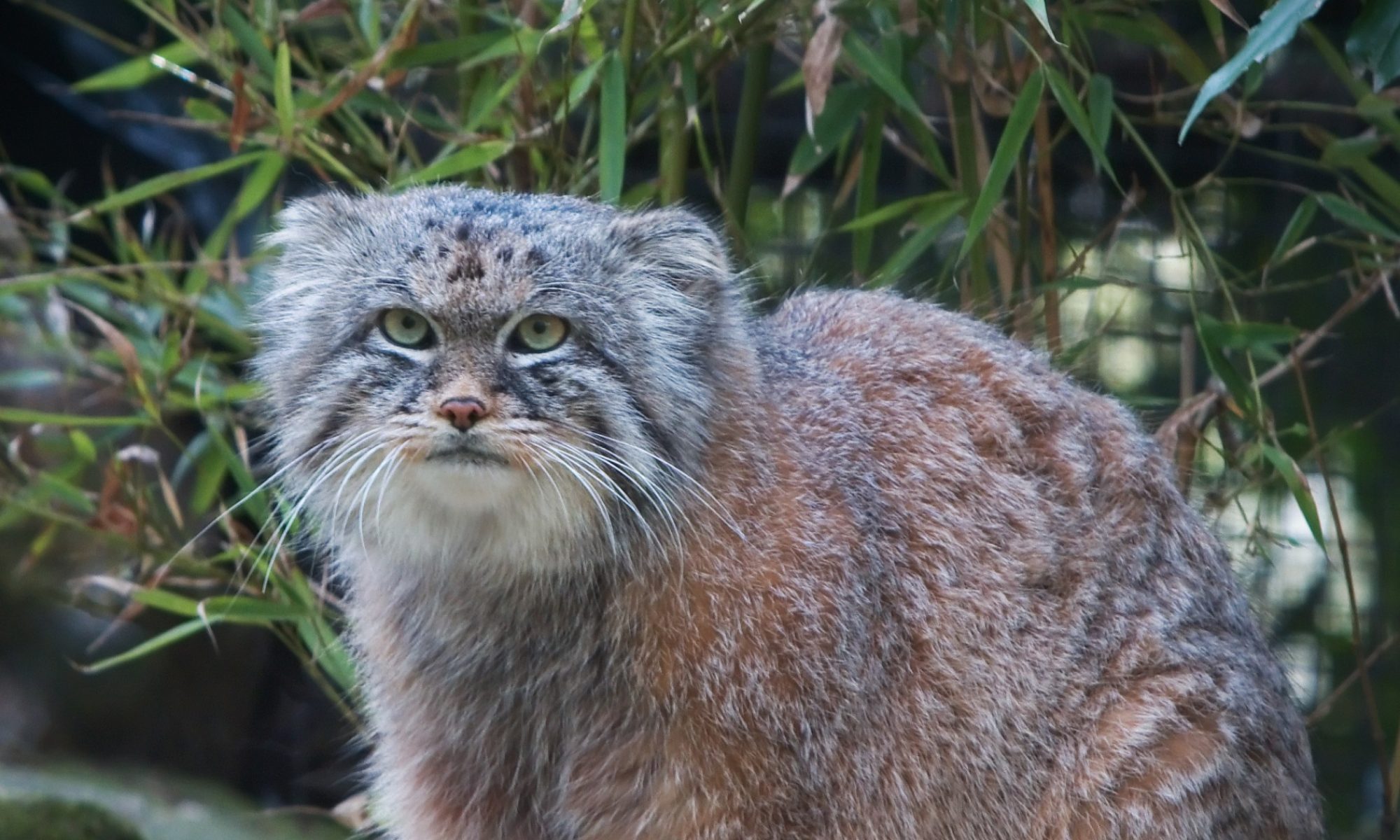
The Jungle Cat or ‘Felis Chaus’ of Asia is known as the ‘reed cat’ or ‘swamp cat’ in Africa. This is probably a more accurate name for this feline, as it rarely strays into jungle regions.
Preferred habitat is anywhere where there is water. Lake margins or riversides which often border dense ground cover are an excellent environment in which to hunt and breed. However the extent of habitation is much wider than this; ranging from desert (where it is found near oases or along dry riverbeds) to grassland, shrubby woodland and dry deciduous forest, as well as cleared areas of forest. They have been observed from sea level up to altitudes of 8,000 ft or more. Jungle cats are distributed throughout Asia, Sri Lanka and India. They are also found in Egypt.
Jungle cats are tenacious and adaptable moving into regions reclaimed by humans , where irrigation and cultivation have been carried out. However the jungle cat is prone to loosing its habitat due to the very same human intervention.
Similar in build to the Serval and the African Wildcat and once thought to be related to the Lynx, Jungle cats are actually a very close relative of the domestic cat. They have long legs and a sleek build but they can grow to quite a hefty 14 Kilograms in weight standing up to 40 cms tall with a length of almost 100 cms. Tails are short though at 20 to 30 cms, with faint rings, and bearing a black tip. A jungle cats coat can range through sandy-brown, reddish or gray, and is unpatterned except for some brown striping on the legs. The ears are tall and rounded and are reddish with short, wide tufts on the tips.
Jungle cats feed mainly on small mammals, principally rodents, (a study in India’s Sariska reserve estimated that jungle cats catch and eat three to five rodent per day). Birds rank second in importance, but in southern Russia waterfowl are the mainstay of jungle cat diet in the winter. With overwintering populations of waterfowl congregating in large numbers on unfrozen rivers and marshes, the jungle cat hunts among reed beds and along edges of wetlands, searching for injured or weakened birds. Other prey species are taken more opportunistically, including hares, nutria, lizards, snakes, frogs, insects, and fish.
Credits: