Cat of the Month ~ January 2012
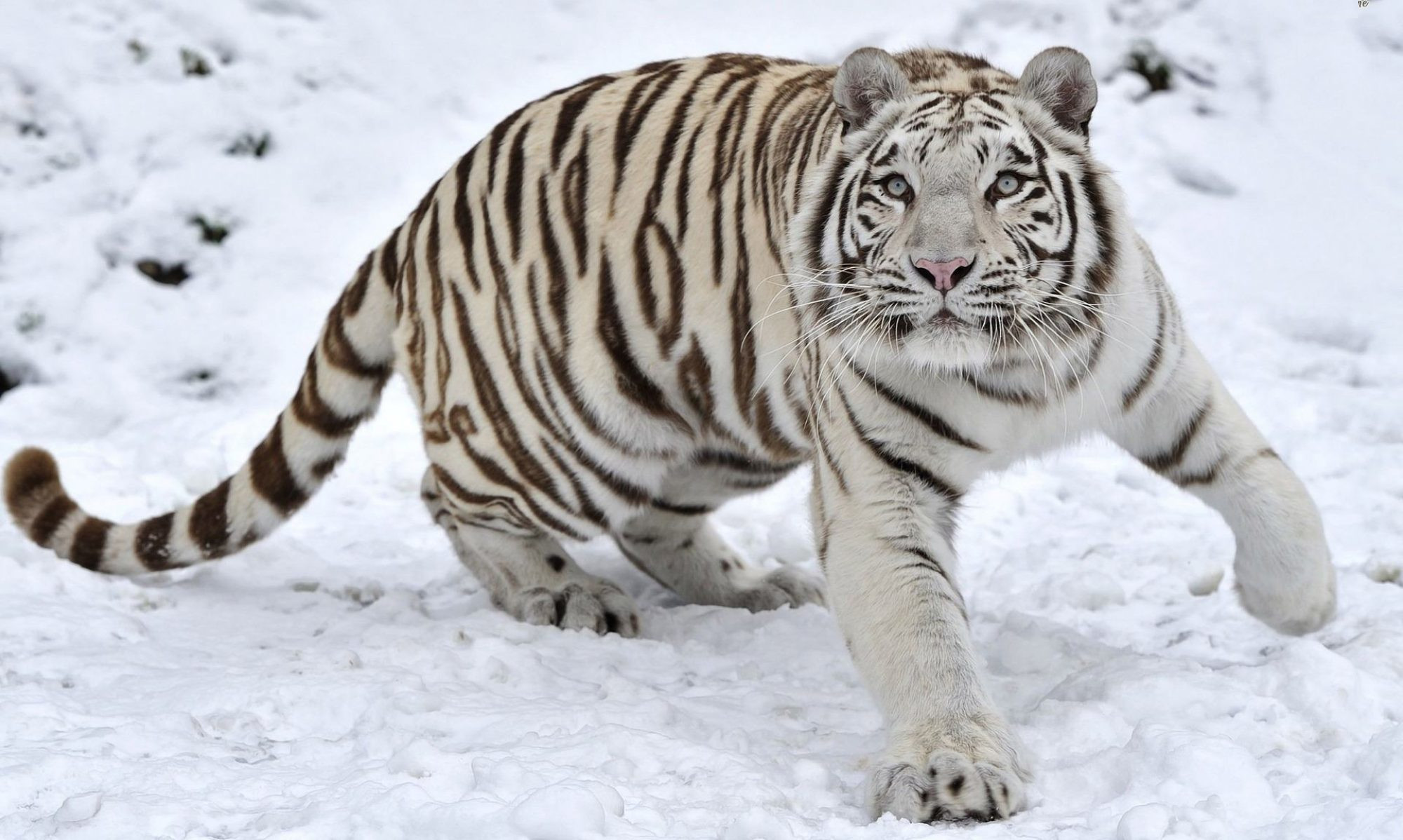
White tigers are basically a colour variant of the Bengal tiger (Panthera tigris bengalensis), and are rarely found in the wild. It is though, reported as having been seen in the wild from time to time in the Assam, Bengal, and Bihar regions of India and especially from the former State of Rewa (in fact home to the very first white tiger). It is believed that all white tigers in captivity in the world today are the descendants of this single white tiger, caught (and named ‘Mohan’) by the Maharajah of Rewa in the year 1951.
The White Tiger is almost identical to the now famous Royal Bengal Tiger except for a genetic mutation that causes a change in the colour of the fur and eyes. The origin of the Bengal Tiger is believed to be from the region we know today as Siberia. From there, these Siberian Big Cats (Panthera tigris altaica) migrated south over the course of thousands of years (and as the climate of their native territory became colder). Today Asia, India and Malaysia all are home to tigers (some of which are white due to genetic mutation), although their numbers are dwindling.
White tigers are only born when two tigers that both carry the unusual gene for white colouring, mate. Unfortunately there are many forced breeding programs currently in progress which are detrimental to those tigers bred in captivity. This is indeed often a sad tale which is outlined in the following very serious and informative article [White Tigers – Conserving Misery]. (Not for the very young or easily upset, Ed)
Where present, white (and other) Bengal tigers will be found regions of dense undergrowth and forested areas where they can camouflage themselves and ambush their prey.
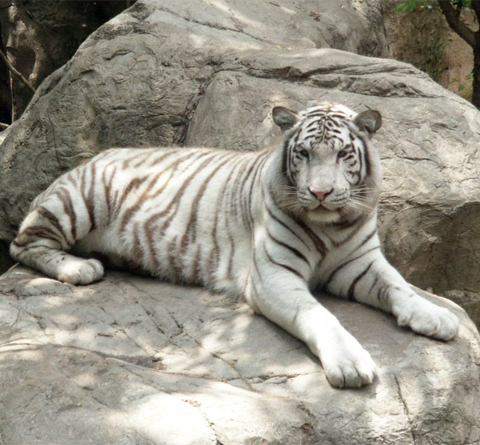
Though, today white tigers are mostly confined in zoos (for example the Nandan Kanan Zoo in Orissa, India) they are also found in many National parks, such as those in India and the Far East.