Cat of the Month ~ January 2011
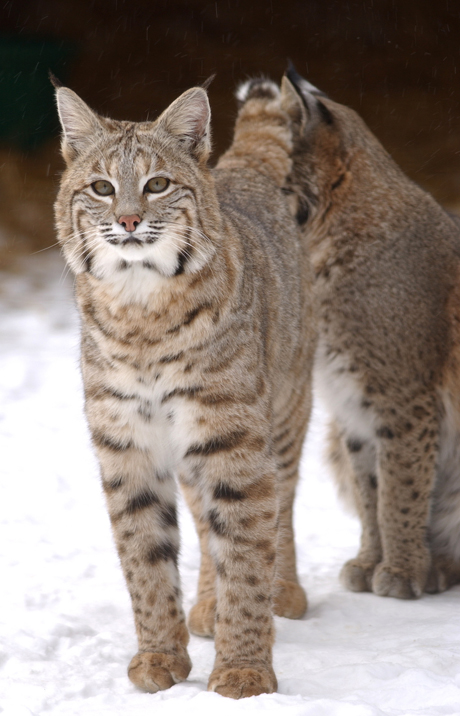
The bobcat (Lynx Rufus) is a North American mammal of the cat family. With twelve recognized subspecies, its habitat ranges from southern Canada to northern Mexico, including much of the continental United States. An adaptable and thriving predator that inhabits mixed deciduous-coniferous and hardwood forests it has a preference for brushy and rocky areas, as well as semi-desert, urban boundaries, and swampland.
A healthy bobcat is strong-bodied, slender and sturdy. It’s a medium-sized feline, with a short, “bobbed” tail (around six inches in length), a prominent face ruff and tufts of black hair on its pointed ears. The sides and flanks are usually yellowish-brown or reddish-brown with distinct or faint black spots. Also it has distinctive black bars on its forelegs. The back is often tawny-coloured with a dark mid-dorsal line. The tail may have one to several indistinct dark bands and a tip that is black on top but which is white on the underside. The coat varies from light ruddy brown through grey to again white on the underbelly (like the tail). With whiskered face and black long-tufted ears the bobcat resembles the other species of the mid-sized Lynx genus. It is smaller than the Canadian Lynx, with which it shares parts of its range, but can grow from four to eight times the size of an average domestic cat, reaching a hefty 40 pounds in weigh and 37 inches long!
The bobcats preferred prey list is extensive, including rabbits, hares, woodchucks, squirrels, chipmunks, mice, voles and other small rodents and birds. It will also hunt anything from insects and reptiles to deer and pronghorn antelope (though usually a weak or injured animal will be chosen). A very strong and aggressive hunter the bobcat may also take small domestic goats or lambs, poultry, small pigs, sheep and house cats, as well as stealing from traps set by humans. It has also been known to eat vegetation, but this is rare. Prey selection depends on location and habitat, season, and abundance (of course).
Bobcats are most active just after dusk and before dawn, when they will inevitably begin the hunt for food. They are secretive, solitary and seldom observed, tending to hunt and travel in areas of thick cover. Bobcats rely on their keen eyesight and hearing (and a tenacious patience) for locating and stalking enemies and prey. Following a kill bobcats may cache, or cover, the body of their prey with leaves, grass or snow. This is a common trait in other feline species that are known to store their kills for future consumption when food is sparse.
[teaserbreak]
Like most cats bobcats are territorial and largely solitary, although they will allow overlap of territory with nearby cats. At its territorial boundaries the bobcat will use claw marks and deposits of urine or faeces as a semi-permanent indicator of its presence. Territorial and home ranges have been shown in studies to vary from eight to twenty square miles in size. Females tend to have smaller and more exclusive ranges than males. Daily movements of one to four miles are common. Bobcat tracks have an overall round appearance with four round toe pads in both front and rear prints. There is a fifth toe on the forefoot; however, it does not leave an impression because it is raised high on the foot. The claws do not leave an impression either because they are usually retracted.
When breeding Bobcats often have more than one mate and do not form lasting pair bonds. They breed between January and May and have a gestation period of about two months. Females may breed before they are one year old but generally do not produce a litter until they are two years old. Dens are located in caves, rock crevices, hollow logs and trees, or beneath windfall. The den may be lined with dry leaves, moss or grass, which is formed into a shallow depression by the female. The same den site may be used for several years in a row. Kittens are born with two to three per litter and their survival is (of course) linked to food abundance. When food is plentiful, many young survive; however a scarcity of food results in heavy mortality to kittens. Kittens weigh 10 to 12 ounces at birth and are born blind (their eyes remaining closed for three to eleven days. Kittens nurse for about 60 days and remain with the female until the following spring. Males do not participate in raising the young. At about four weeks of age, kittens begin to leave the den and take solid food provided by the female. Juvenile bobcats leave the females territory before she gives birth to a litter the following year.
Historically bobcats have not been protected from human destruction, as they were for many years viewed as a threat to agriculture and more desirable game species. In addition, deforestation in many regions has reduced the habitat available to bobcats (and indeed to many other cat breeds and wildlife species throughout the world). Though Bobcats don’t necessarily need mature forest to thrive they do flourish in areas with thick undergrowth. A further concern in the 1970s was a large increase in the value of bobcat pelts. This raised concerns that they could be over hunted but (fortunately) at that time the bobcat was reclassified as a protected fur bearer in many regions, with more controlled hunting and trapping seasons. Conversely, housing and commercial development have decreased the amount of suitable habitat further still!
Although the bobcat has been subject to extensive hunting by humans, both for sport and fur, its population has proven to be resilient and stable. This elusive predator features in Native American mythology and the folklore of European settlers. Bobcat attacks on people are virtually unknown and they are not a significant carrier of disease. Hopefully this majestic creature to behold will continue to live alongside us in their often hidden retreats.




 We have been invited to share some of our wisdom and experience with you all and are not a little flattered and certainly very pleased with the prospect.
We have been invited to share some of our wisdom and experience with you all and are not a little flattered and certainly very pleased with the prospect.












